BPE Tokenizer
BPE Training Example (inefficient yet valid logic for understanding)
Assignment 1 给了一个用于理解 BPE 流程的简单的处理过程,我将其形成了相应的代码,但是相对低效,BPE 的训练流程及代码如下:( 所处理的文本见代码 )
- Vocabulary Initialization: 初始化一个 256+1 大小的字典,前 256 为 0-255 每个字节的表示 第 257 个 token 为 特殊 token
<|endoftext|>; - Pre-Tokenization: 将文本进行预分词,避免导致类似 "dog!" 和 "dog." 语义相近,但分词结果完全不同的情况,此处使用直接的
split函数,一般而言可以使用正则的手段进行(后续); - Merges: 每一轮,计算每个元组中相邻元素组成的新 pair 的频率,选择频率最大的(相同频率时,选择字典序大的)pair 进行合并,作为引入的新 token,经过 $N$ 次迭代(超参数,此处使用 $N=6$)
from typing import Dict
from collections import Counter
text = """low low low low low
lower lower widest widest widest
newest newest newest newest newest newest
"""
def init_vocab() -> Dict[str, int]:
"""256 byte + <|endoftext|>"""
vocab = dict()
for i in range(256):
item = {
f"{chr(i)}": i
}
vocab.update(item)
eot = {
"<|endoftext|>": 256
}
vocab.update(eot)
return vocab
def pre_tokenization(text):
text_split = text.split()
text_counter = Counter(text_split)
return dict(text_counter)
def pair_count(cand_list):
status = Counter()
for cand in cand_list:
cand_key = list(cand.keys())[0]
cand_value = list(cand.values())[0]
for i in range(len(cand_key) - 1):
# i: [0,1,2] i+1: [1,2,3] ❌
# i: [0,1] i+1: [1,2] ✅
pair = (cand_key[i], cand_key[i + 1])
status[pair] += cand_value
return dict(status)
def merge(pair_counted, cand_list):
# 频率相同时,选择字典序大的
max_freq = max(pair_counted.values())
max_pairs = [pair for pair, freq in pair_counted.items() if freq == max_freq]
max_cnt_pair = max(max_pairs)
new_cand_list = []
for cand in cand_list:
cand_key = list(cand.keys())[0]
cand_value = list(cand.values())[0]
# 判断 (a, b) slice 是否在 x1,x2,...xn 中,保持邻近顺序
is_in = any(cand_key[i:i+len(max_cnt_pair)] == max_cnt_pair for i in range(len(cand_key) - 1))
if is_in:
new_key = []
i = 0
while i < len(cand_key):
if cand_key[i:i + len(max_cnt_pair)] == max_cnt_pair:
new_key.append("".join(max_cnt_pair))
i += len(max_cnt_pair)
else:
new_key.append(cand_key[i])
i += 1
new_key = tuple(new_key)
new_cand_list.append({new_key: cand_value})
else:
new_cand_list.append({cand_key: cand_value})
return new_cand_list, max_cnt_pair
if __name__ == '__main__':
num_merges = 6
vocab = init_vocab()
pre_tokenized = pre_tokenization(text)
merges = []
for word, count in pre_tokenized.items():
item_key = tuple(list(word))
merges.append({
item_key: count
})
new_tokens = []
for _ in range(num_merges):
pair_cnt = pair_count(merges)
merges, new_token = merge(pair_cnt, merges)
new_tokens.append(new_token)
print(merges)
print(new_tokens)
new_tokens = ["".join(item) for item in new_tokens]
print(new_tokens)
for token in new_tokens:
vocab_size = len(vocab)
vocab[token] = vocab_size
print(vocab)
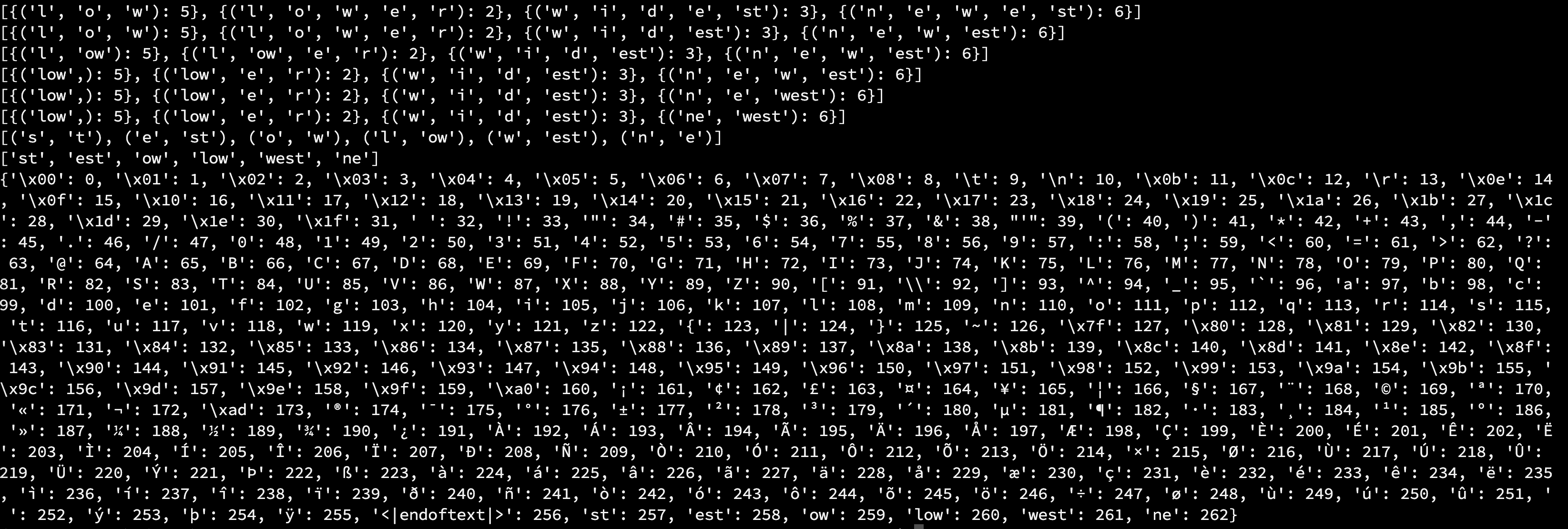
如下图 1 所示为相应的运行结果,其中代码中有步骤级的打印结果
BPE Tokenizer Training (efficient implementation)
Reference
[1] CS336 Assignment 1 (basics): Building a Transformer LM. Version 1.0.5
Contact
There may be some errors present. If you find any, please feel free to contact me at wangqiyao@mail.dlut.edu.cn. I would appreciate it!